
- SSH PROXY TUNNEL WITH A DIFFERENT USER NAME HOW TO
- SSH PROXY TUNNEL WITH A DIFFERENT USER NAME SOFTWARE
- SSH PROXY TUNNEL WITH A DIFFERENT USER NAME FREE
With openssh package version 7.4p1-11 or later, we can use ProxyJump option to transfer files using a proxy server. SCP through a proxy server Method-1: Using scp with ProxyJump
SSH PROXY TUNNEL WITH A DIFFERENT USER NAME HOW TO
Additionally, visit /learning-explorer to become an Oracle Learning Explorer.įor product documentation, visit Oracle Help Center.In this tutorial we will learn how to SSH or SCP through a proxy server (jump host)
SSH PROXY TUNNEL WITH A DIFFERENT USER NAME FREE
More Learning ResourcesĮxplore other labs on /learn or access more free learning content on the Oracle Learning YouTube channel. All of them together show how, through SSH port forwarding, you can access and avail of a remote system’s services. Note that while the lab exercises demonstrated SSH tunneling by using the Cockpit service, this video uses VNC and web services for its examples. The video tutorial Using SSH Tunnels With Oracle Linux 8 gives more examples for configuring different types of SSH tunnels. The ol8-server’s Overview page is displayed.īy using the Cockpit web console, you can remotely manage the instance even though the service itself is not exposed on any public facing network. Log in by using oracle as the user name and password. This time, the Cockpit login screen appears for the ol8-server instance. Return to your browser and change the URL to access ol8-server’s Cockpit service as if you were accessing it locally.

sleep specifies a waiting period in seconds that the tunnel waits for a connection before the tunnel closes.-f indicates that the connection is forked into the background.-N prevents the execution of remote commands.Ssh -L 9090:localhost:9090 can use optional arguments in the command syntax, such as the following: The -L option maps a port on the local host to a port on the server. On the terminal window, open an SSH connection to ol8-server by using local port forwarding. Note that the connection does not succeed. On a browser, open the Cockpit web console to ol8-server through its IP address. Verify the inaccessibility of the Cockpit service. If you are currently connected to the ol8-server in a terminal window, type exit to disconnect from the instance. Note: Unless instructed otherwise, all the commands must be typed from your SSH client desktop. The instance is running a firewall service.The instance is preconfigured to run the Cockpit service.Typically, if you want to run the Cockpit web console for a system that is connected to the Internet, the service would be exposed on a public facing network, which is not advisable.įor this demonstration, the ol8-server is configured for security as follows: This configuration enables you to access services on the remote system that are otherwise inaccessible because the services might be running behind a firewall or might not be listening on a public network interface.Ĭockpit is a good example of such a service. Local port forwarding over SSH maps a local port on the client system to a remote port on the server system. In addition, alternative methods might be preferable than using SSH tunnels for this purpose. However, these are beyond the scope of this tutorial. Other mechanisms can be used to force all TCP traffic through your SSH connection. The -D option indicates that the connection uses dynamic port forwarding.Įxport _proxy="socks5://localhost:8080"
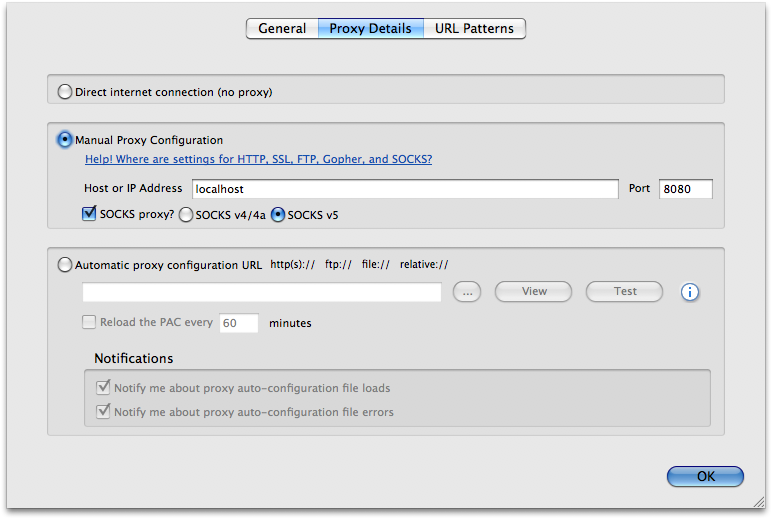
Open an ssh connection to ol8-server while using the -D option and specifying a port number to use locally. If you are currently connected to ol8-server in a terminal window, type exit to disconnect from the instance.Īlternatively, open a new tab for a separate terminal window. Note: Unless instructed otherwise, you must run all the commands in this section from your SSH client desktop.
Configuring SSH dynamic port forwardingĭynamic port forwarding enables communications across a range of ports by making SSH act as a SOCKS proxy server. Note: When using the free lab environment, see Oracle Linux Lab Basics for connection and other usage instructions.
SSH PROXY TUNNEL WITH A DIFFERENT USER NAME SOFTWARE
A client system with appropriate software installed, such as a desktop viewer to use VNC services.A remote SSH system with the some configured services, such as web services, VNC services, Cockpit, etc to be used by remote clients.This tutorial teaches you how to configure the following types of SSH tunneling: This tutorial is targeted at users of Oracle Linux 8 or later. SSH tunnels or SSH forwarding encapsulates specific TCP traffic and enables it to traverse the network through an SSH connection. This tutorial provides step by step procedures to configure SSH tunnels for network traffic. When completing your lab, substitute these values with ones specific to your cloud environment.Ĭonfiguring SSH Tunnels in Oracle Linux Introduction It uses example values for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure credentials, tenancy, and compartments.This tutorial is available in an Oracle-provided free lab environment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
